Gut/Liver-on-a-chip models
Where two intercommunicating organs are more powerful than one
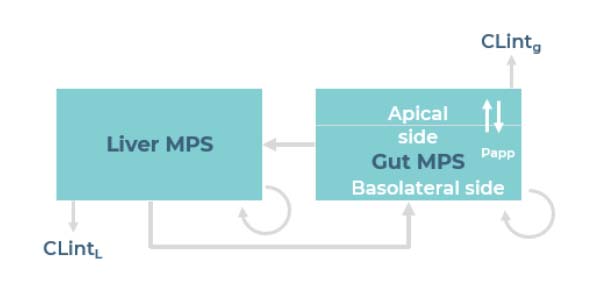
Our in vitro human Gut/Liver models, (also known as microphysiological systems) are cultured in Multi-chip Dual-organ plates by the PhysioMimix® Multi-organ System.
They emulate the dynamics of drug absorption through the intestinal barrier and subsequent hepatic metabolism. Ideal for predicting oral bioavailability or organ-organ crosstalk studies.
Access the model via our PhysioMimix® Bioavailability assay kit: Human 18, which contains a fully validated SOP, primary human cells, media and plates. All models are available via our ADME Contract Research Services.
Why use our Gut/Liver-on-a-chip models?

Complement in vivo studies
Inform in vivo study design with human-relevant insights. Circumvent cross-species limitations
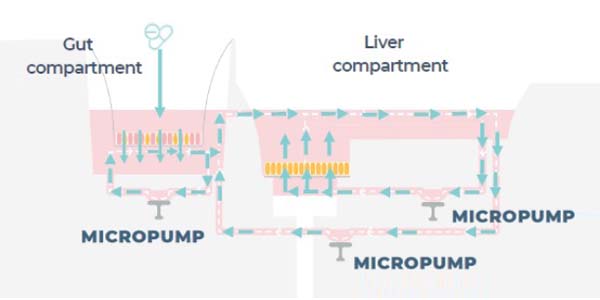
Fluidic flow
Organ-specific flow in each chamber provides essential nutrients, O2 and biomechanical stimuli to promote culture longevity
Organ-to-organ crosstalk
Facilitate cellular communication by fluidically interconnecting the gut & liver chambers

Gut and liver-specific markers
QC measurements before and after compound dosing to confirm microtissue functionality and viability
Flexible assay design
Primary cell and immortalized cell line compatibility. Study individual organ and combined contributions to drug metabolism

Combine with computational modeling
Combine experiments with computational methods for improved human predictive potential
Mimic oral or IV drug routes
Dual-organ plate design enables the modeling of two drug administration routes to inform which is most suited

High inter- and intra-plate reproducibility
Model reproducibility delivers robust and reliable data for confidence in human ADME predictions
One multi-organ model, two variants
Two gut models, cultured on standard 24-well Transwell® inserts, are available for interconnection with our primary hepatocyte (Liver-on-a-chip) model. The functionality of both organs is maintained in co-culture.
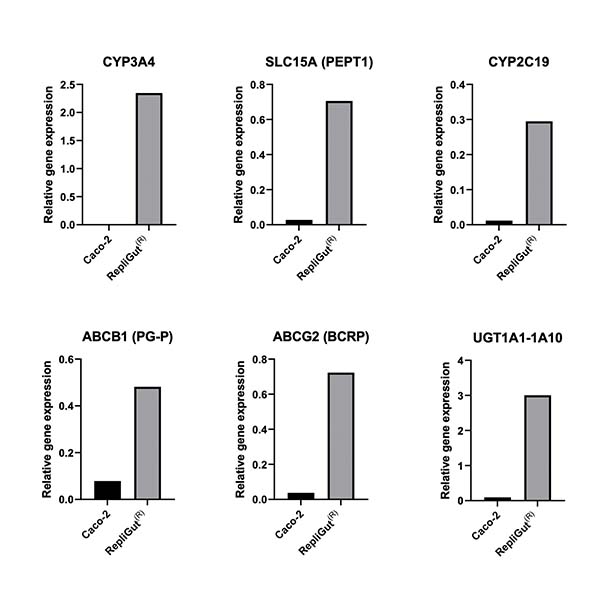
1. RepliGut®-Planar Jejunum model
A primary human jejunum crypt-derived model for physiologically relevant metabolism and transporter gene function.
View more information in this application note
2. Caco-2 model
This enables data comparability with a commonly used in vitro model of drug absorption.
Dynamic intra-organ crosstalk
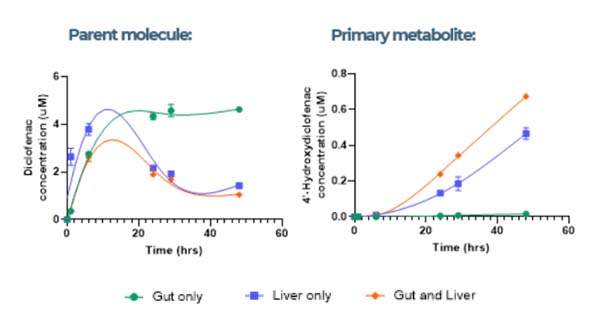
Our model can be operated as gut only, liver only or in combination.
Interconnecting the two organs via fluidic flow enables the dynamic study of crosstalk between the organs.
Intestinal permeability can be predicted for insights into drug absorption. Clearance parameters from the gut and liver can be estimated from both the parent drug and its metabolites.
Utilize data derived from the model to generate compound concentration versus time graphs and area under the curve (AUC) measurements. Determine the individual and combined contribution to drug metabolism by the gut and the liver.
Translate in vitro data into in vivo predictions
Estimate the in vivo pharmacokinetic parameters of orally administered drugs by combining Gut/Liver-on-a-chip with in silico computational modelling tools.
Fully validated Gut/Liver-on-a-chip models
| Gut/Liver model | Cell type | Applications | Required products |
|---|---|---|---|
| Immortalized gut/primary liver cultures | Gut: Caco-2 cells and HT-29 goblet cells Liver: Primary human hepatocytes | Drug Metabolism Drug Bioavailability | PhysioMimix Multi-organ System, Dual organ plates, 3D validated cells |
| Primary human gut/ human liver cultures | Gut: primary human jejunum crypt epithelial stem cells Liver: primary human hepatocytes | Drug Metabolism Drug Bioavailability | PhysioMimix Multi-organ System, Bioavailability assay kit: Human 18 |
Gut/Liver-on-a-chip Applications
Frequently asked questions
How long can the Gut/Liver-on-a-chip model be used?
The length of an experiment will depend on the application, for example, drug metabolism studies are typically shorter than studies focussing on organ crosstalk. The gut model is pre-cultured in static conditions to achieve a fully differentiated monolayer, then added to the dual-organ plate in co-culture with primary human hepatocytes. For ADME applications drugs are dosed for between 48- and 72-hours with periodic media sampling taken to quantify drug concentration.
Does the gut tissue in your model generate villi and/or crypt-like structures?
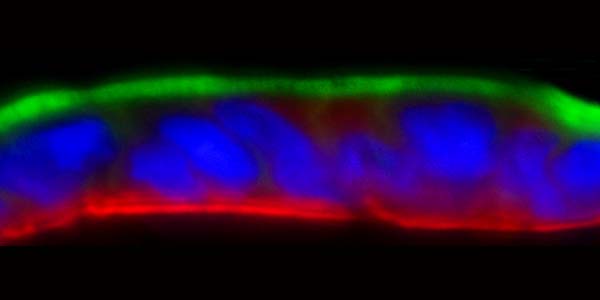
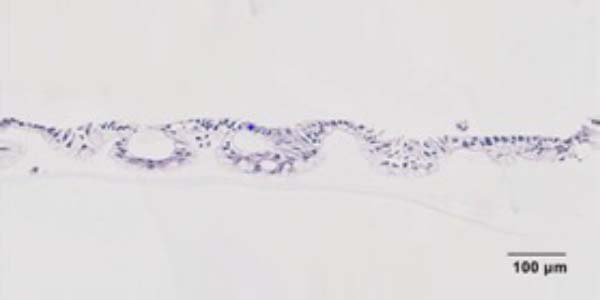
Our Caco-2/HT-29 gut microtissues display similar tight junction formation, mucus secretion and metabolic function to in vivo gut tissue. The microtissues in perfused culture mimic the 3D shape of in vivo gut villi, but they are not recreated to the same depth.
For the primary Gut/Liver-on-a-chip model, intestinal epithelial stem cells are expanded and then differentiated to form a polarized monolayer that expresses tight junction proteins. All major cell lineages are achieved including goblet cells that are mucus-producing.
How do you measure gut barrier permeability? Can you measure TEER?
The permeability of barriers can be assessed in several ways, measuring the transepithelial electrical resistance (TEER) is a common one. This provides a quantitative estimation of the barrier strength and integrity. We can also measure the permeability of molecules of different sizes, to estimate the extent of passive diffusion allowed by the cell barrier. Whereas TEER measurements are taken throughout the experiment to monitor cell barrier growth and differentiation, permeability tests are carried out at the end, to confirm the stability of the barrier post drug dosing.
Do you need to use a common media for the Gut/Liver-on-a-chip model?
For the co-culture of primary gut and liver tissues, we have developed a specialized/proprietary media that maintains the functionality of both cell types during crosstalk and ADME studies. This will be one of the components of a future ‘in-a-box’ kit that will contain all media, cells, OOC plates and assays to enable Gut/Liver studies in your lab.
Is there a physical exchange of liquids and/or nutrients between the two organs?
Media in the gut apical compartment is separated by the gut barrier with media that circulates between the gut basolateral and liver compartment. Nutrients and drug compounds can diffuse through the gut barrier by either passive or active diffusion. Liver microtissue will be exposed to drugs absorbed by gut tissue, likewise, the gut tissue will be exposed to metabolites released by the liver tissue, reproducing an in vivo-like crosstalk between the two organs.
Are the flow rates within the gut and liver models and between the models independently controlled to be in line with physiological flow rates?
Yes, we have adopted a programmable approach which enables flow rates and profiles (pulsatile or continuous) to be individually tuned within the gut and liver chambers to mimic each organ’s exposure to the fluid shear forces and dynamic mechanical stresses that occur in vivo. This is achieved through robust materials, tightly controlled pneumatics and micropumps embedded into the Multi-chip Dual-organ plates which accurately and reliably move media around tissue structures or between organ mimics for weeks to maintain the performance of that culture over extended periods of culture. Please watch the on-demand webinar: The Rhythm of Life for a detailed explanation.
What type of cells are used in the Altis Biosystems RepliGut® model and how does it work?
Altis Biosystems source and expand region-specific intestinal epithelial stem cells from human tissue. Biobanked cells are seeded onto a semi-permeable membrane (Transwell®) coated with a biomimetic scaffold. Within seven to eight days of culture, you get a fully differentiated, polarized jejunum epithelium with basal and apical cell access. The tissue is then inserted into the barrier compartment/chamber of our Multi-chip Dual-organ plate. For more info on their model, please visit the Altis Biosystems website.
Why can I only access the Altis Biosystems version of your Gut/Liver-on-a-chip model via your ADME Contract Research Services?
We are currently developing an in-a-box solution complete with a fully validated SOP, common media, Multichip Dual-organ plates and all the 3D validated cells required so that you can recreate our fully human multi-organ model in your laboratory with ease. Whilst we work on a commercialized kit, you can access the model/submit molecules for testing via our ADME Contract Research Services. In the interim, the Caco-2 immortalized gut in vitro model, in combination with our primary hepatocyte liver model, enables you to get started within your laboratory, validate the approach and benefit from insights into the contribution to drug metabolism by the gut and liver when these two organs are connected to better inform in vivo studies.
Can you quantify mucus formation? If so, how?
Mucus can be visualised by histology of the gut barrier or immunofluorescence staining of mucin proteins. For quantification, there are commercially available ELISA kits to quantify mucus production.
What are the main readouts of the Gut/Liver-on-a-chip model?
Tissue-specific readouts can be obtained during the pre-culture of gut barrier and liver tissue. Once the two organs are connected into a fluidically-linked system, additional readouts enable the effects of crosstalk to be measured (please visit the Bioavailability and Drug Metabolism Application pages for more info). For liver tissue, the main readouts are CYP3A4 activity and albumin. For gut tissue, the main readouts are TEER and permeability to assess barrier integrity. When in co-culture there is >2mL of circulating media, which provides plenty of material to quantify protein concentration using ELISA or other metabolomic-based assays. RNA from both tissue types can be extracted for transcriptomic studies.
Are the cells seeded in the PhysioMimix Multi-chip Dual-organ plates?
For the gut tissue, cells are pre-seeded on Transwells and then expanded and differentiated before addition to the dual-organ plate. Primary human hepatocytes are seeded directly onto collagen-coated scaffolds in the liver compartments of the Dual organ plate.
Visit the Bioavailability Application page to visualize the timeline
If you do not find the answer to your question listed, please contact us