How does Hepatitis B virus infection cause human disease?
It is difficult to replicate the complexity of the liver using cell lines and primary human hepatocyte cultures. The specificity of HBV means that few suitable animal models exist. The lack of suitable model systems limits the study of HBV and the development of new therapeutics.
HBV attacks the liver and can cause both acute and chronic disease. It is one of the most common infectious diseases globally and the inflammation caused by HBV can lead to cirrhosis, impaired liver function, and an increased risk of liver cancer.
Traditional 2D cell lines and animal models such as humanized liver mice don’t provide long-term, highly functional liver models that replicate the physiological environment needed for HBV infection.
Our solution
The primary human hepatocyte cultures in our Liver-on-a-chip can be infected with HBV and maintained for at least 40 days, enabling the recapitulation of the entire HBV life cycle.
Infection with viral inoculum leads to long-term expression of antigens and viral DNA, allowing the anti-HBV response of drugs across a range of modalities to be evaluated.
The PhysioMimix® HBV Assay shows increased expression of NTCP, the liver bile acid transporter that is key to initiating the HBV infection in the liver, which is not present in 2D models. This assay also provides greater cumulative increases in the HBV surface antigen replicating the in vivo environment more closely.
Innate immune and cytokine responses after infection with HBV mimic those observed in HBV-infected patients. This allows the study of pathways that are important for immune evasion and the validation of biomarkers.
Studying HBV
Limitations with current techniques
- Infection of primary human hepatocytes requires high multiplicity of infection (MOI)
- Few systems allow the study of immune response and host/pathogen interactions
- Cancer cell lines expressing HBV have limited physiological relevance
- Humanized mouse models are fragile, slow, and expensive
Advancements with PhysioMimix OOC
- Stable culture at reduced MOI
- Enables detailed longitudinal analysis of hepatocytes, non-parenchymal cells, and circulating immune cells
- Primary hepatocyte model expresses full liver function and complete HBV life cycle
- Human models available in days not months
End point measurements
Longitudinal and endpoint measurements include (but not limited to):
Functionality biomarkers
- Cytochrome P450 enzyme activity
- Albumin production
- Urea production
Profiling analysis
- Lactose dehydrogenase (LDH) release
- Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
- Cell viability
- Inflammatory response profiling
- Cytokine & chemokine immunoassays
- Confocal microscopy
- Transcriptomics:
- Cellular phenotypes
- Viral receptor expression
- Genetic perturbations
Infection biomarker
Quantification using microscopy / qPCR / immunoassay of:
- Viral antigen
- HBV DNA
- HBV pgRNA
- HBV cccDNA
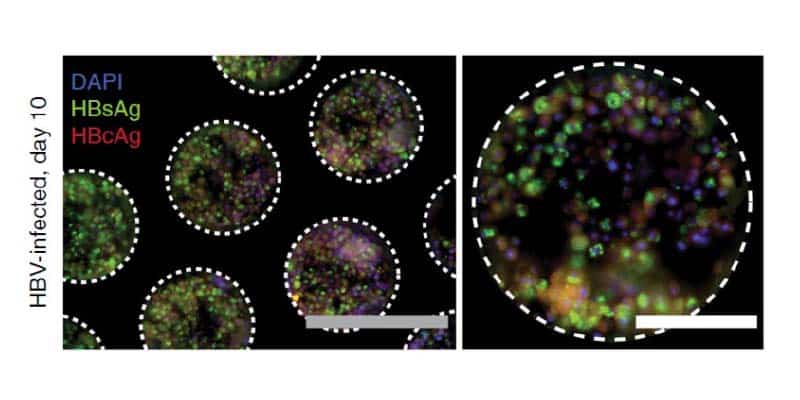
Infected liver microtissues recapitulate the complete HBV lifecycle
Following 10 days post-infection Hepatocyte and Kupffer cell microtissues are stained for the expression of HBV surface antigen (HBsAg – green) and HBV core antigen (HBcAg – red).
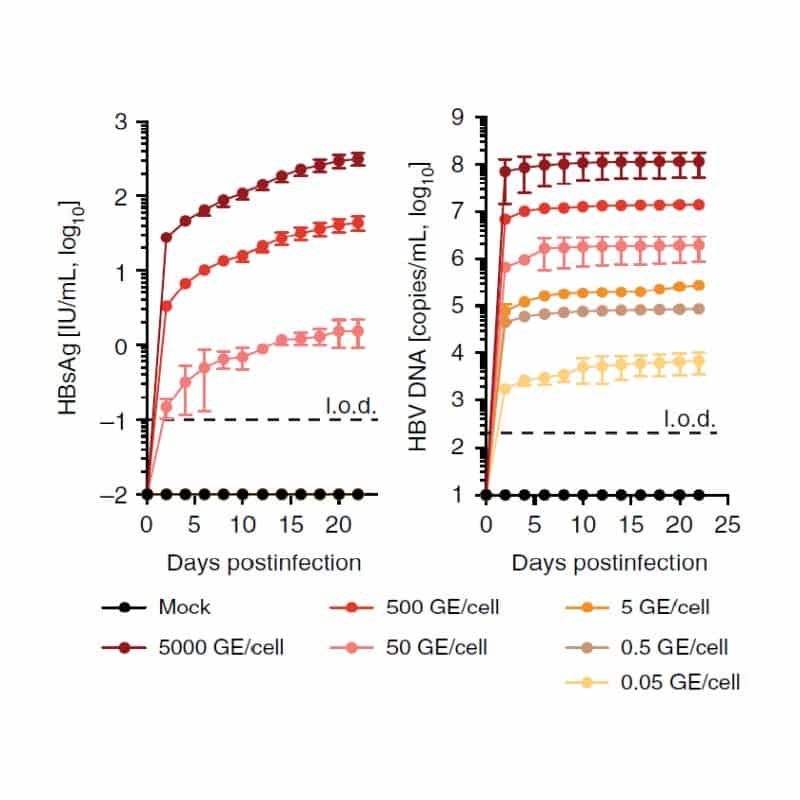
HBV infection can be launched from multiple sources of virus
Increasing levels of virus inoculum launch varying degrees of infection within the liver microtissues as assessed by the production of HBV surface antigen (HBsAg) and secreted HBV DNA.

Add PhysioMimix OOC into your lab
Harness the power of PhysioMimix OOC in your own lab with the purchase of a single- or multi-organ microphysiological system. With a growing community of users and support from our experts, there has never been a better time to transition into 3D cell culture.