Part of the wider CRACK IT scheme – the multi-challenge competition aims to leverage CN Bio’s existing OOC expertise – our MPS development and optimization knowledge and our leading Liver-on-a-Chip model.
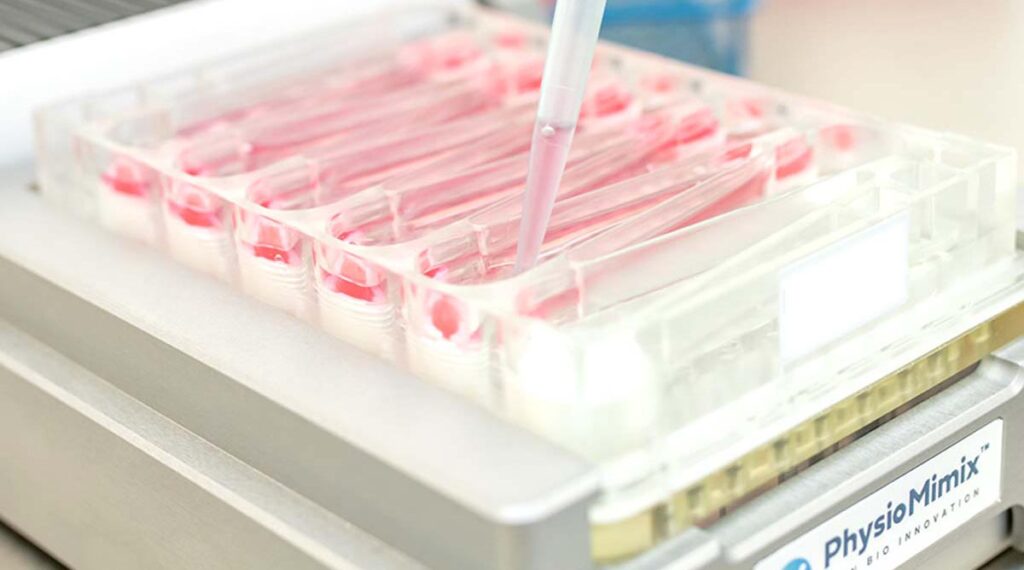
Image: PhysioMimix® Liver-on-a-Chip model
We’re excited to announce that NC3Rs, a UK-based scientific organization dedicated to helping the research community worldwide to replace, refine, and reduce (3Rs) the use of animals in research and testing, has selected us to join Phase I of its SensOoChip challenge, aimed at improving the utility and reproducibility of connected OOC models by integrating real-time multiparametric monitoring – all part of our mission to reduce reliance on animal testing! This is a three-phase mega-challenge, with funding for up to five years, is sponsored by several high-profile names in the industry, including AstraZeneca, Bayer AG, GSK, Merck Healthcare KGaA, Novartis, and UCB.
The SensOoChip challenge is part of the organization’s wider CRACK IT scheme – a multi-challenge competition that funds collaborations between industry, academia, and SMEs to advance research into the 3Rs and the development of new alternative methodologies (NAMs).
Kicking things off with an initial 9-month project, the Challenge aims to capitalize on the advances already made in the OOC field; focusing on three core objectives that will utilize our expertise in the development of microphysiological systems and our industry-leading Liver-on-a-Chip model:
- Integration of real-time, multiparametric monitoring of an established liver OOC system to increase the quantity and quality of data collected
- Connection and monitoring of a second organ – the heart
- Demonstration that the multiparametric datasets generated can be interrogated and modeled to improve understanding of the local physiological environment, reproducibility of OOCs, and the effect of drug administration
Real-time multiparametric monitoring of OOC models is a key milestone in the journey to fully understanding the microenvironment, gaining deeper insights into ADME and toxicity studies, and developing more advanced disease models. A core part of the project will be the development of minimally invasive sensors that collect an array of data from the OOC model. When integrated into a heart/liver multi-organ model, the sensors will provide key information for studies such as cardiotoxicology – a principal cause of drug failures.

Project lead
The project at CN Bio will be led by one of our talented Lead Scientists, Dr Emily Richardson.
Stay tuned for further updates as the Challenge kicks off!

