How can you predict altered drug responses due to underlying disease?
Inflammation in the liver can arise following a variety of insults. Inflammation can change liver biology and frequently makes hepatocytes more sensitive to insults from hepatotoxicants.
Immune-mediated toxicity is challenging to predict as the root cause is not related to a drug’s mechanism of action or structure, and adverse reactions only occur in a subset of patients.
Most models do not have the complexity to allow the co-culture of liver cells with immune cells. Nor do they allow long enough cultures to explore chronic inflammation effects or disease states on immune-mediated toxicity.
Our solution
By incorporating immune cells into PhysioMimix® organ-on-a-chip (OOC) models, detailed mechanistic studies of the condition in the presence of various inflammatory cues and disease can now be performed to flag susceptibility risks.
Although not exclusive to the liver, this is where adverse reactions are most prevalent. Using the PhysioMimix Immune-mediated DILI Assay, co-cultures of human hepatocytes and immune cells are exposed to the drug of interest in the presence or absence of immuno-stimulation. The model can be used to identify adverse effects on hepatic health and function or changes to the inflammatory profile.
The effects of single acute dose responses or chronic treatment regimens over multiple weeks can be assessed and compared to better predict drugs that induce immune-mediated effects.
Using PhysioMimix disease models, drugs can also be tested in the presence of common liver disorders such as Hepatitis B and NAFLD/NASH to identify patient cohorts with increased DILI susceptibility due to the presence of underlying inflammatory disease.
Studying immune-mediated toxicity
Limitations with current techniques
- Challenging to study immune-tissue level interaction in vitro
- Poor in vitro to in vivo data translation
- Unable to recapitulate inflammation driven by disease
- Challenging to run acute and chronic exposure assays due to shortlived cultures
Advancements with PhysioMimix OOC
- Immune cells can be incorporated into and circulate around liver microtissues
- Measurement of clinical biomarkers (e.g. ALT/AST) allows for direct comparison to in vivo data
- Inflammation can be induced through disease state e.g. NAFLD/NASH
- Long-term stable tissues enable repeat compound dosing
End point measurements
Longitudinal and endpoint measurements include (but not limited to):
Functionality biomarkers
- Cytochrome P450 enzyme activity
- Albumin production
- Urea production
Clinical liver heath biomarkers
- Lactose dehydrogenase (LDH) release
- Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
- Aspartate Transferase (AST)/Alanine amino transferase (ALT)
Optional profiling analysis
- Quantitative PCR
- Transcriptomics
- Immunoassays
- Inflammation (e.g. IL-6, IL-8 TNF-α)
Flagging enhanced DILI risk due to inflammation
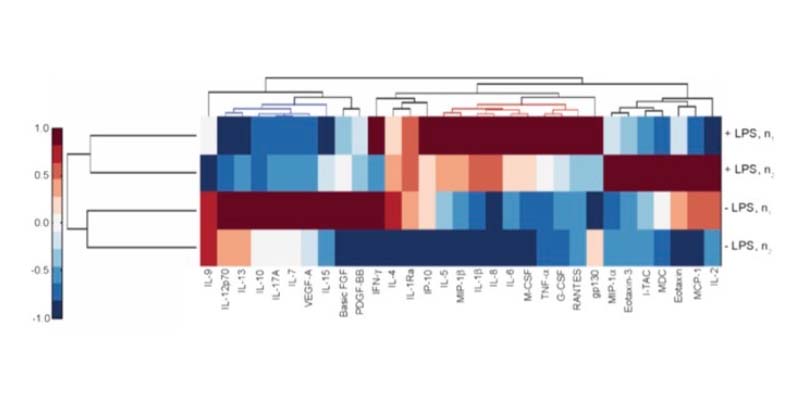
The effect of inflammation on DILI sensitivity can be assessed by testing therapeutics in the PhysioMimix Inflammatory-mediated DILI Assay with or without specific immunomodulators (e.g., LPS).
Immune-mediated toxicity
Following exposure to pro-inflammatory stimuli, liver microtissues produce a range of physiologically relevant cytokines, chemokines, and growth factors that can be altered using different stimuli or inducing disease states.
Access our DILI Service
Get instant access to the immune-mediated DILI Assay via our CRO Service. Through a collaborative approach, our experts work with you to plan and execute your study.
Bespoke projects are carried out by our dedicated team of scientists in our CRO facility providing you with actionable data within weeks.
Add PhysioMimix OOC into your lab
Harness the power of PhysioMimix OOC in your own lab with the purchase of a single- or multi-organ microphysiological system.
With a growing community of users and support from our experts, there has never been a better time to transition into 3D cell culture.