Brochures & Flyers

Organ-on-a-chip Contract Research Services Brochure
Discover our full range of Organ-on-a-chip contract research services including ADME, NASH, DILI and Oncology as well as all the relevant endpoints.
Articles
ADME Studies: Determining Promising Drug Compounds
Dr Abbas discusses factors that can affect the outcome of an ADME study, signs that a drug compound shows promise, red flags, and key parameters to determine safety and efficacy.
This article is taken from PharmTech, November 2022.
Articles

How to Keep Breathing – The Future of Inhaled Medication Testing
Dr Emily Richardson discusses the current challenges faced to bring inhaled therapeutics to the market and the potential of Organ-on-a-Chip to increase positive outcome by improving ADME drug testing.
This article is taken from International Biopharmaceutical Industry, Summer 2022.
Videos and animations
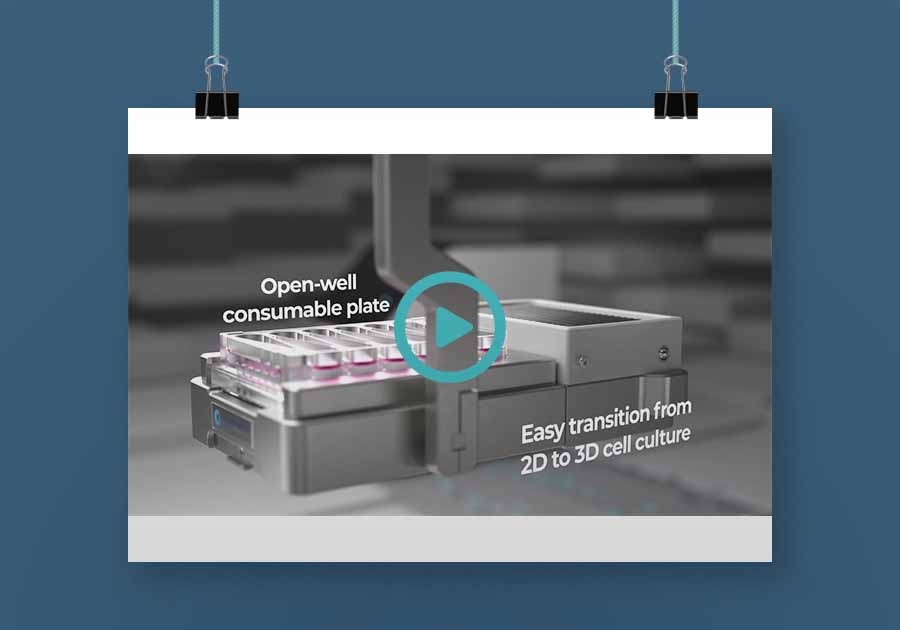
PhysioMimix Multi-organ System Animation
An introduction to the CN Bio PhysioMimix Multi-organ System. This animation demonstrates how our microphysiological system works, how to create a Gut/Liver-on-a-chip model and an example of its use in determining drug Bioavailability in vitro.
Scientific publications

Application of a gut–liver-on-a-chip device and mechanistic modeling to the quantitative in vitro pharmacokinetic study of mycophenolate mofetil
Milani et al., 2022
This study shows how an in vitro gut-liver multi-organ model can quantitatively recapitulate the in vivo metabolism of a drug. By combining Organ-on-a-chip with in silico modeling, the study also demonstrates the potential of multi-organ models for quantitative estimation of PK parameters of a drug and its metabolites.
Posters
Normalization of organ-on-a-chip samples for mass spectrometry based proteomics and metabolomics via dansylation-based assay
Gallagher et al
This poster shows the combined use of MS-based proteomics and metabolomics with organ-on-a-chip to better assess the classification of biological replicates in toxicity studies.
Posters
Harnessing the power of multimodal imaging to explore ASO distribution in cells, complex in vitro models and tissue
Alex et al
This recent poster from GSK and collaborators features data from our PhysioMimix® OOC and Liver (MPS-LC12) plates. The results demonstrate that the distribution of ASOs into Kupffer cells and circular or cuboidal hepatocytes cultured in 3D can be detected using imaging.
Scientific publications

Exploration and Application of a Liver-on-a-Chip Device in Combination with Modelling and Simulation for Quantitative Drug Metabolism Studies
Docci et al., 2022
This publication explores the potential of the PhysioMimix liver model for investigating drug candidates for hepatic disease. This study integrates mathematical modeling with experimental liver-on-a-chip studies and demonstrates how this approach supports the generation of high-quality data from complex in vitro cellular systems.
Scientific publications

Multiorgan microphysiological systems as tools to interrogate interorgan crosstalk and complex diseases
Trapecar, 2022
A review of the state of multi-organ microphysiological systems in 2021. Overviews of currently available multi-organ MPS and the different technologies, cells and physiological cues used. Discusses approaches for systems biology integration and how MPS can be more readily adopted in the wider research community.
Application notes

Improved prediction of oral bioavailability using a gut-liver microphysiological system
Abbas, Kostrzewski & Hughes
Central to the development of new drugs is an understanding of their pharmacokinetic properties, in particular their bioavailability. Here, we demonstrate the potential of a true 2-organ gut-liver MPS to better predict human bioavailability and improve in vitro to in vivo correlation.
Application notes

Drug metabolism in a gut-liver microphysiological system
Abbas, Kostrzewski & Hughes
Studies investigating the efficacy and safety of candidate drugs use a variety of animal models to translate research from the bench to clinical trials and then to the clinic. Here, we demonstrate the potential of multi-organ MPS models for improved predictions of in vivo drug absorption and hepatic clearance rates.
Posters
Microphysiological systems of the human liver, gut and linked liver-gut, to assess human drug absorption, metabolism and bioavailbility
Kostrzewski et al
This poster demonstrates the potential of human MPS models for liver, gut, and multi-organ (connecting gut with liver) for the investigation of human PK parameters, drug absorption and metabolism, and bioavailability.

